An Intelligent Ann-Based Framework for Predicting Employee Attrition in Imbalanced Data Scenarios
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58190/icisna.2025.141Keywords:
Intelligent Systems, Artificial Neural Network, Imbalanced Dataset, Adaptive Synthetic Sampling (ADASYN), Employee AttritionAbstract
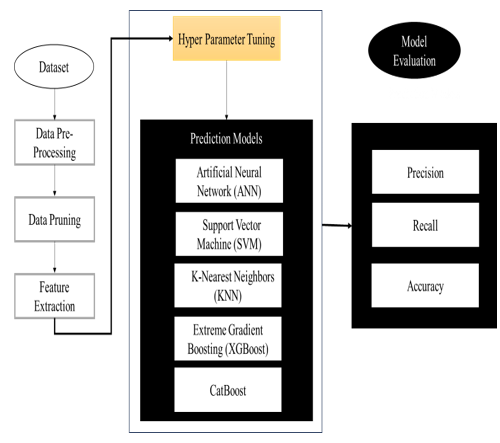
Employee attrition poses a significant threat to organizational stability and performance. While intelligent systems offer a powerful solution, predictive accuracy is often hindered by the inherent challenge of imbalanced data, where the number of employees who stay far exceeds those who leave. This study proposes a novel intelligent framework for employee attrition prediction that directly addresses this data imbalance. We conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of six machine learning algorithms: Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Decision Tree, CatBoost, and XGBoost using a dataset of 1,410 employee records. To enhance model performance and mitigate imbalance, we implemented rigorous hyperparameter tuning and the Adaptive Synthetic Sampling (ADASYN) technique. Our results demonstrate that the ANN model significantly outperformed its counterparts, achieving the highest predictive accuracy and F1-score. The model identified key attrition drivers, including frequency of illness, monthly income, and overtime work, corroborating existing literature on the primacy of well-being and compensation. This research not only validates ANN as a superior intelligent system for this critical business application but also provides organizations with an actionable, data-driven framework for identifying attrition risks and implementing targeted retention strategies.